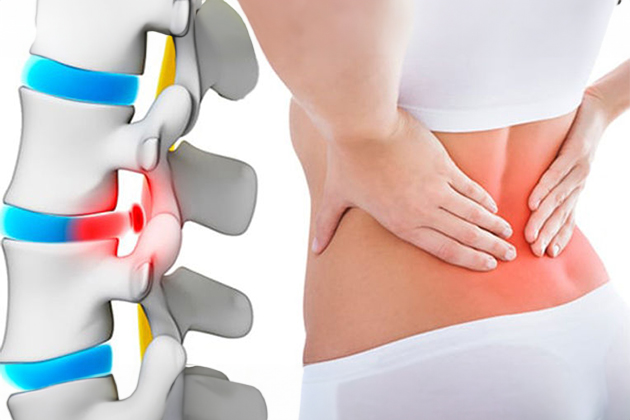
What is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis?
Lumbar spinal stenosis is a condition that occurs when the spinal canal narrows. The vertebrae are bony structures that protect the spinal cord and nerve fibers. The spinal cord and nerve fibers descend from the base of the head through the canal in the middle of the vertebrae. Discs are structures between the vertebrae that help connect them. As we age, discs lose fluid and harden, shifting towards the spinal canal and narrowing its diameter. The growth of facet joints behind the vertebrae and thickening of ligaments can also contribute to this narrowing.
Symptoms of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
The symptoms of lumbar spinal stenosis include:
- Pain, numbness, and cramps in the lower back or legs that worsen with prolonged standing and walking.
- Weakness and numbness in the legs after walking for a limited period, leading to the need to stop and squat.
- A progressive decrease in walking distance.
- Symptoms lessen or disappear with bending or sitting.
If these symptoms are present, it is essential to consult a doctor and undergo tests such as MRI, CT scan, and EMG.
Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Medical Treatment:
- Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications are used.
- Spinal injections, particularly corticosteroids administered in the epidural space or joint space, can be given.
Physical Therapy:
- Due to the tendency to avoid movement, physical therapy or strengthening exercises for the abdomen, back, and legs are recommended.
- Swimming can be included in these activities.
- The goal of treatment is to maintain quality of life and control pain.
Surgical Treatment:
- Lumbar Decompression: A surgical procedure to relieve pressure by enlarging the canal diameter. Minimally invasive microsurgical techniques using a microscope are preferred.
- Laminectomy: Removing the bones at the back to widen the narrowed bony canal.
- Hemilaminectomy and Bilateral Flavectomy: Removing bones only on one side to widen the canal.
- Spinal Fusion: Spinal fusion surgery is performed to ensure stability between vertebrae. Vertebrae are stabilized using titanium screws and various materials.
The surgical success rate is over 65%. Patients usually stay in the hospital for a few days and can return to all activities within 6-8 weeks.
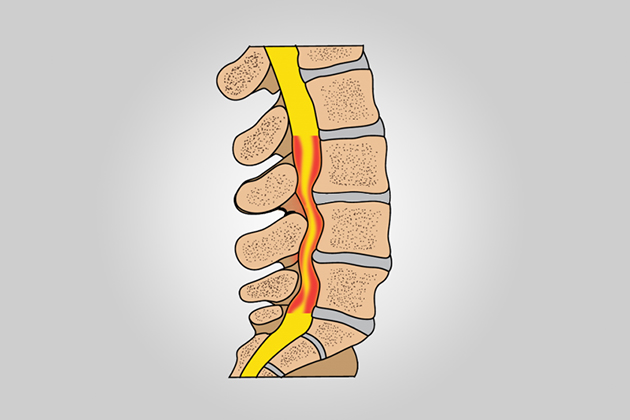
Symptoms of Cervical Canal Stenosis
The symptoms of cervical canal stenosis include:
- Neck and arm pain.
- Weakness in the arms and legs.
- Clumsiness in movements done with hands (inability to open a door handle, button a shirt, open a jar lid).
- Weakness in the legs and difficulty walking.
- In advanced cases, inability to walk without assistance.
- In rare cases, loss of bladder and bowel control.
Diagnostic Methods for Cervical Canal Stenosis
Diagnostic methods include:
- MRI: Shows spinal cord compression due to cervical canal narrowing in detail.
- CT: Used to evaluate bony outgrowths.
- EMG and Nerve Conduction Studies: Help differentiate peripheral nerve compressions.
- SEP: Shows spinal cord compression.
Treatment of Cervical Canal Stenosis
Medical Treatment:
- Pain relievers and injections can be used.
Surgical Treatment:
- Decompression surgeries are performed to eliminate pressure on the spinal cord. Surgical methods include laminectomy, laminoplasty, and fusion surgery.
Prognosis of Cervical Canal Stenosis
More than half of the patients show improvement after surgery. Advanced age, severe neurological deficits, multiple level compression, long-term neurological deficits, narrow canal diameter, and signal changes within the spinal cord negatively affect the prognosis.
Featured Videos
Frequently Asked Questions
Spinal canal stenosis is the narrowing of the spinal canal, which results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. This condition usually develops due to degenerative changes associated with aging, such as osteoarthritis, disc herniation, or spinal injuries.
The symptoms of spinal canal stenosis vary depending on the location and severity of the narrowing. Narrowing in the lumbar region can cause back and leg pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs, and cramps while walking. Narrowing in the cervical region can lead to neck pain, numbness, or weakness in the shoulders, arms, or hands, reduced fine motor skills, and balance issues.
Cervical canal stenosis can cause nerve root compression (radiculopathy) or spinal cord compression (myelopathy) in the cervical region.
The recovery process varies depending on the type of surgical intervention performed and the patient’s overall health condition. Post-surgery, physical therapy and rehabilitation are important to accelerate the healing process and strengthen the spine. Post-operative care includes adhering to the prescribed exercise program, using prescribed medications for pain management, and avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous activities.