What is Spinal Stenosis?
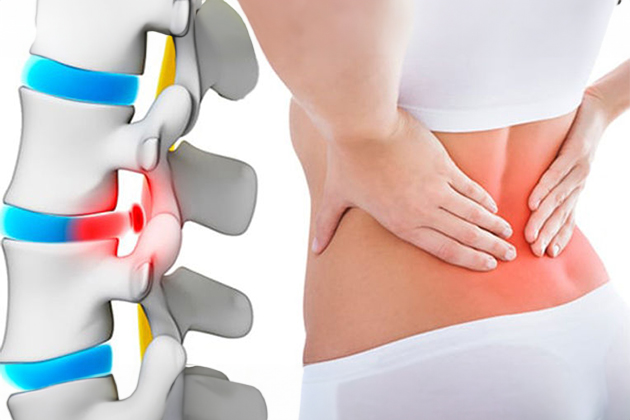
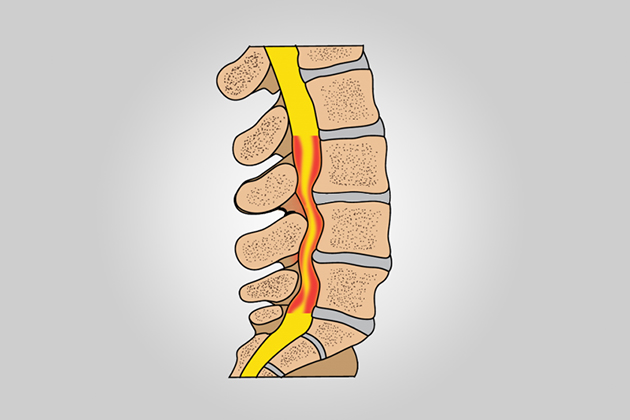
Spinal stenosis is a condition caused by the narrowing of the spinal canal, which houses the spinal cord and nerve roots. This narrowing can compress the nerves, leading to impaired function of the nerves in the affected area. It most commonly occurs in the lumbar and cervical regions.
Symptoms
- Back and Neck Pain: Especially pain that worsens with movement.
- Numbness in Legs and Arms: Tingling, numbness, and weakness in the legs and arms due to nerve compression.
- Difficulty Walking: The need to stop walking due to pain and weakness in the legs.
- Bladder and Bowel Problems: Issues with bladder and bowel control in advanced cases.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: The physician assesses the patient’s complaints and medical history.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): The most effective method for accurately identifying the narrowing in the spinal canal.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Used primarily to evaluate the bone structure.
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures the electrical activity of nerves and muscles.
Treatment
Non-Surgical Treatment Methods
- Physical Therapy and Exercises: Exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles around the spine and increasing flexibility.
- Medication Therapy: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: Steroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain in the spinal canal.
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight control, proper posture, and ergonomic adjustments.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment is considered for patients with severe nerve compression symptoms or those who do not respond to other treatment methods. The goal of surgical intervention is to reduce the pressure on the nerves and improve the patient’s quality of life.
- Decompression Surgeries:
- Laminectomy: Removing part of the vertebral bones called the lamina to widen the spinal canal.
- Foraminotomy: Widening the openings where the nerve roots exit the spine.
- Fusion Surgeries:
- Spinal Fusion: Permanently joining two or more vertebrae. This increases spinal stability but may reduce mobility.
- Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques:
- Microsurgery: Surgical methods involving smaller incisions and less tissue damage.
- Endoscopic Surgery: Less invasive surgical techniques using a camera.
Post-Surgery
- Rehabilitation: Post-operative physical therapy and rehabilitation help the patient recover more quickly and effectively.
- Pain Management: Pain relievers and other medications to control post-operative pain.
- Regular Follow-Up: Regular doctor visits to monitor the healing process after surgery.
If spinal stenosis is not treated timely and appropriately, it can severely impact the quality of life. Both surgical and non-surgical treatment options are evaluated and applied based on the patient’s condition. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help patients maintain their daily activities and relieve pain.
Frequently Asked Questions
Symptoms vary depending on the location and severity of the stenosis. Lumbar (lower back) stenosis is characterized by back and leg pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs. Cervical (neck) stenosis can cause neck pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the shoulders, arms, or hands, reduced fine motor skills, and balance problems.
Spinal canal stenosis is diagnosed based on the patient’s complaints and physical examination findings. Imaging methods such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), CT (Computed Tomography), and X-rays are used to confirm the diagnosis and determine the location and severity of the stenosis.
Treatment options are divided into non-surgical and surgical methods. Non-surgical treatments include physical therapy, pain relievers, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), epidural steroid injections, and brace use. Surgical treatment options include laminectomy, laminotomy, discectomy, spinal fusion, and minimally invasive surgical methods
The recovery process after surgery varies depending on the type of surgical intervention and the patient’s overall health status. Following physical therapy and rehabilitation programs is crucial during the recovery period. Postoperative care includes adhering to the prescribed exercise program, using medications for pain management, and avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous activities. Regular follow-ups and compliance with the doctor’s instructions are also very important.