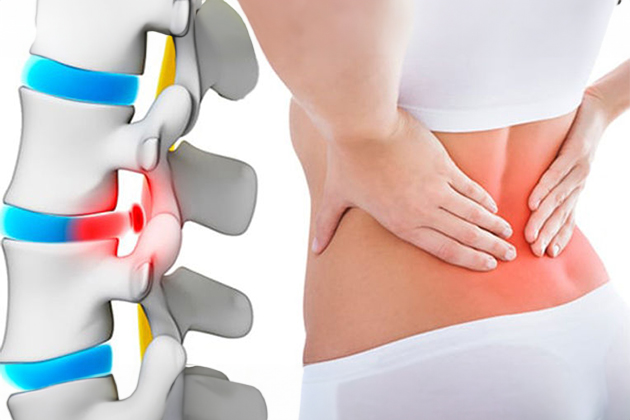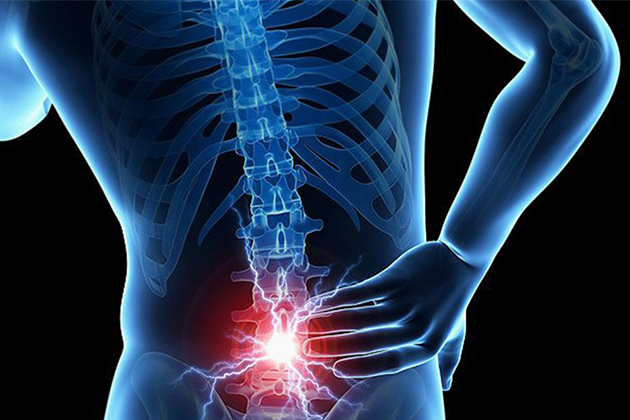
What is Lumbar Spondylolisthesis?
Spondylolisthesis is the condition where one vertebra slips forward over the vertebra below it. This can lead to spinal instability and pressure on the nerve roots, resulting in pain and neurological symptoms.
Causes of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
- Degenerative: Wear and tear of spinal discs and joints due to aging.
- Congenital: Congenital spinal abnormalities.
- Traumatic: Accidents or sudden injuries.
- Pathological: Bone tumors or other diseases.
- Isthmic: Stress fractures in the spinal bone.
Symptoms of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
- Lower back and leg pain
- Numbness or tingling in the legs
- Muscle weakness
- Gait instability
- Stiffness in the back or lower back
- Pain that worsens with forward bending
Diagnosis and Treatment of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
Diagnosis:
- Physical Examination: The doctor evaluates the patient’s symptoms and examines spinal movements.
- Imaging Methods: X-ray, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), and CT (Computed Tomography) scans are used to determine the degree of vertebral slippage and pressure on the nerve roots.
Treatment:
Non-Surgical Treatment Options:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the supporting muscles of the spine.
- Pain Relievers: NSAIDs, muscle relaxants.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: To reduce nerve root inflammation.
- Brace Use: To support the spine.
Surgical Treatment Options:
- Spinal Fusion: Fusing two or more vertebrae to stabilize the slipped vertebrae.
- Decompression: Removing part of the vertebra or discs to reduce pressure on the nerve roots.
Frequently Asked Questions
Spondylolisthesis is the medical term for the slipping of one vertebra over another. It is usually seen in adults as a result of the aging process but can also occur in young people due to hereditary spinal issues or trauma. Spondylolisthesis generally occurs in the lower back and can lead to leg pain if it compresses nerves.
Muscle Weakness or Balance Problems: Imbalanced or weak muscles can prevent vertebrae from staying in place.
Disk Degeneration: Issues with spinal joints, particularly problems in the isthmus part of the facet joint.
Fractures and Traumas: Breaks or traumatic injuries to the vertebrae can lead to spondylolisthesis.
Congenital Anomalies: Congenital spine anomalies can cause spondylolisthesis.
Aging: Degeneration of the spine with age can cause vertebral slippage.
Genetic Factors: A family history of spondylolisthesis can increase the risk.
Back and Lower Back Pain: Pain in the back or lower back which can increase over time.
Numbness and Tingling: Compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots can lead to numbness or tingling in the legs.
Muscle Weakness: Spondylolisthesis can cause weakness in the leg muscles and walking difficulties.
Spinal Curvature: Advanced spondylolisthesis can lead to spinal curvature (scoliosis).
Urinary and Fecal Incontinence: Rarely, it can cause loss of bladder or bowel control.
Nerve Compression: Pressure on nerve roots can cause radicular pain.
Medications: Painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, or muscle relaxants may be prescribed.
Physical Therapy: Physiotherapists create personalized exercise programs to strengthen muscles and increase flexibility.
Exercise: Special exercise programs to improve spine stability, reduce pain, and enhance muscle strength.
Spinal Supports: Use of back braces or special devices.
Injection Treatments: Steroid or local anesthetic injections provide temporary relief.
Surgical Treatment: Considered in severe cases where other treatments are ineffective. Surgery aims to relieve nerve compression, protect the spinal cord, and restore spinal stability.
Laminectomy: Removal of the back part of one or more vertebrae to reduce pressure.
Fusion: Use of devices or bone grafts to close the gap between two vertebrae and stabilize them.
Micro Surgery: A surgical approach with smaller incisions and quicker recovery time.
Spondylolisthesis treatment varies based on the patient’s overall condition and symptoms. It is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment option for each patient.